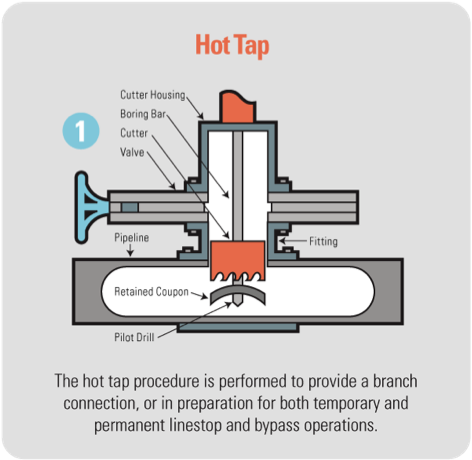
Hot tapping is a process for creating a new branch connection to an existing pipeline or tank while the system is still in service and pressurized. Typically, a weld-on or bolt-on saddle is attached to the pipe with a flanged outlet. A flanged valve is bolted onto the saddle, and a pressure-tight tapping machine attached to the valve. Next, the tapping machine bores into the pipeline. Once the tap is completed the valve is closed, the tapping machine is removed, and the new branch connection is now live.
The American Petroleum Institute RP2201 is a compilation of best practices and standards for Hot tapping in the petrochemical industry. Its authority dictates how to perform this service safely and correctly. An instructive flow chart in the standard is titled “Is the use of a Hot Tap Appropriate”.
After determining a Hot Tap is necessary, the next step is finding the best provider to fit your needs. There are important questions to consider when choosing a provider:
RJ Stacey can provide the right answers to these questions and more. We have extensive training and years of field experience, as well as access to the industry’s most innovative equipment and unparalleled field support.
RJ Stacey’s large collection of tapping machines, drive units, sub adaptors, specialty cutters and pilots guarantee that we’ll only use equipment designed and rated for any specific job.
.500” through 48” hot tap cutters.
Sub adaptors class: 150# #300 #600 #900
Pressure Ratings: up to 2300psi
Temperature Rating: Cryogenic to 700°F- up to 1000°F available special circumstances
Boring bar travels up to 120”
Size on Size pipe, Reduced Branch, Tangential (Angle) Taps, Flat tank taps, Taps into fittings, elbows, blind flanges, Extreme flow rates, Extreme temperatures
Potable water, Mill Water, Hydrocarbons, Acids/Caustics, Process Chemicals, Solids/PCI, Wastewater, Steam
Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Special Alloys, Concrete Lined/Reinforced, Fiberglass, HDPE, PVC, Red Copper, Ductile/Cast